I-PEX Inc. (Headquarters: Kyoto City, Kyoto Prefecture, Representative Director: Takaharu Tsuchiyama, Tokyo Stock Exchange Prime Market Code: 6640, hereinafter I-PEX) is developing a human safety detection sensor called “Smart Cloth,” a proximity sensor that is versatile enough to be used with any robot, including human collaborative robots, and can detect the proximity of approximately 15 cm to prevent contact between robots and humans.
I-PEX has offered the Electrostatic Capacitance Torque Sensor “ESTORQ®” as a solution for the coexistence of humans and robots, and “Smart Cloth” will be added to this lineup.
“Smart Cloth” was exhibited at the “36th Manufacturing World (Tokyo),” which took place at Tokyo Big Sight from Wednesday, June 19th to Friday, June 21st, 2024, and is scheduled to be released in 2024.
 Depiction of human safety detection sensor “Smart Cloth”
Depiction of human safety detection sensor “Smart Cloth” Invitation to Measure/Test/Sensor Expo at Manufacturing World 2024 [Tokyo]
Background of the development of “Smart Cloth”
Our product, “ESTORQ®,” is a torque sensor for human collaborative robots and other related robots to detect contact between a human and a robot, and stop the robot when it comes into contact. Our clients, robot manufacturers, have asked us to develop a product to stop the robot before it comes into contact with a human.
Although proximity sensors in the form of hard cover and sheet types are available on the market, they are not widely adopted in robot manufacturing because they have limitations for versatile use due to the variety of shapes and kinds of robots.
Focusing on conductive cloth, that allows electricity to pass through, we have decided to develop “Smart Cloth.” This product has exclusive characteristics such as the elasticity and the flexibility of cloth material. Moreover, it is versatile to be reshaped and used multi-purposely, and it is easy to install on existing robots.
Expected uses of “Smart Cloth”
“Smart Cloth” is intended to be used to reduce and avoid the risk of dangerous contact between humans and robots and other related incidents.
In particular, attaching “Smart Cloth” to the end effector would help to avoid the risk of contact at the tip of the robot since sensors to detect contact with humans do not exist on the end effectors of human collaborative robots.
The anticipated uses are as follows:
- Contact avoidance for service robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs)
- End effector contact avoidance
- Door entrapment prevention
- Robot proximity detection
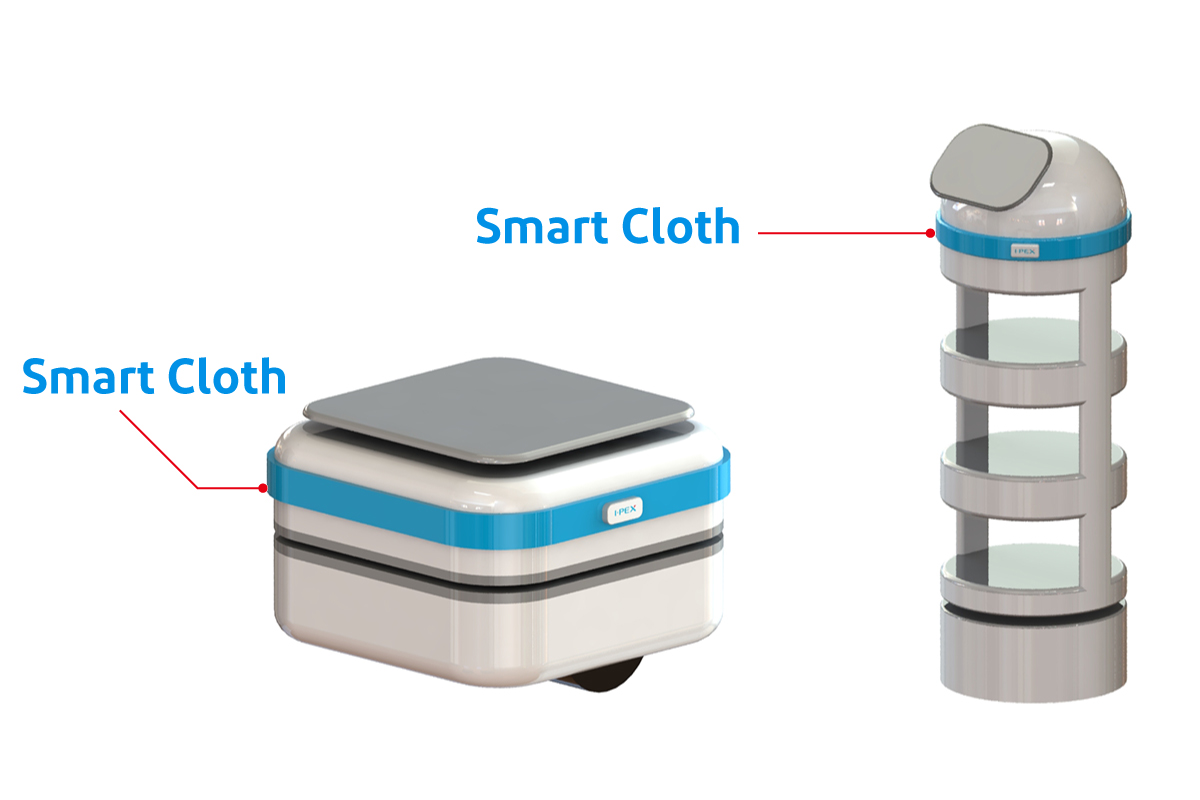 Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” on a service robot, AGV, and AMR
Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” on a service robot, AGV, and AMR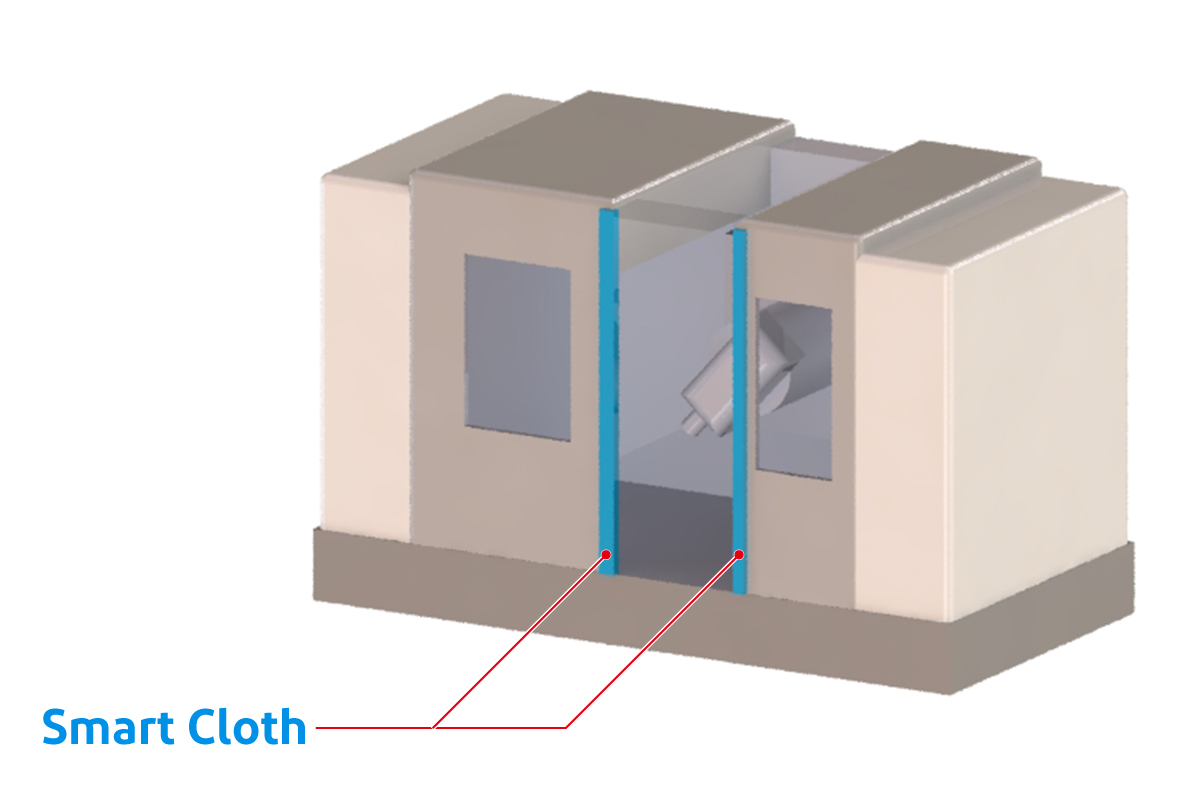 Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” to prevent door entrapment
Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” to prevent door entrapment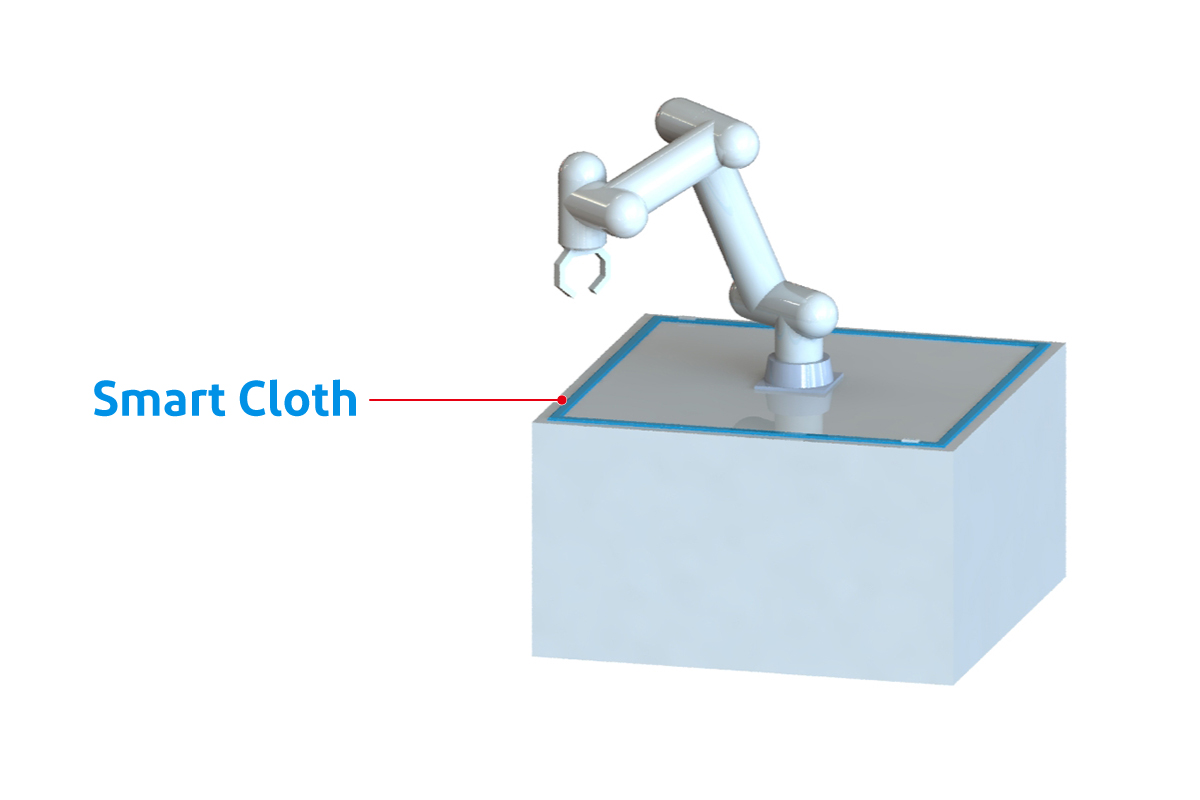 Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” for robot proximity detection
Depiction of the use of “Smart Cloth” for robot proximity detection



