I-PEX Inc. (Headquarters: Kyoto City, Kyoto Prefecture, Representative Director and President: Reiji Konishi, hereinafter I-PEX) is developing an advanced conductive mesh that will contribute to enhancing next-generation lithium battery performance by improving the adhesion and conductivity of silicon-based active materials.
Actual samples of this technology and technical explanation materials will be exhibited at the I-PEX booth (6F No. 15) at the 66th Battery Symposium Co-exhibition, to be held at Winc Aichi in Aichi Prefecture from Tuesday, November 18th to Thursday, November 20th, 2025.
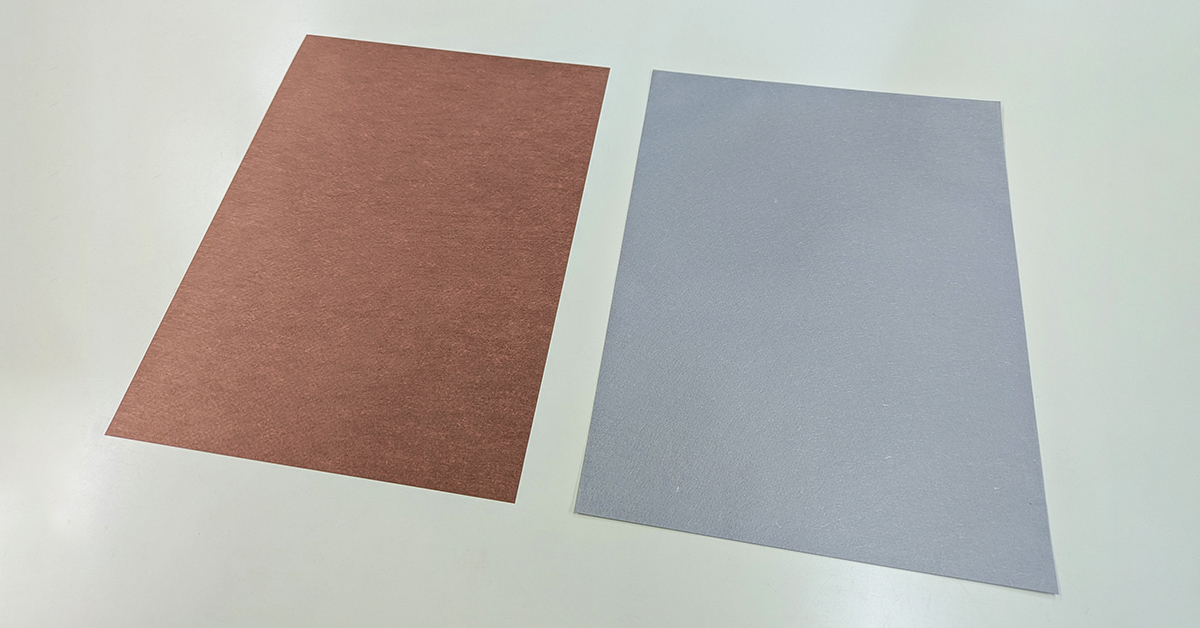
 Advanced Conductive Mesh (left: copper-metallized product, right: aluminum-metallized product)
Advanced Conductive Mesh (left: copper-metallized product, right: aluminum-metallized product)Development Background
Recently, to increase the capacity of next-generation lithium-ion batteries, silicon-based active materials—whose theoretical capacity is more than ten times that of graphite-based active materials—are expected to be used. However, silicon-based active materials undergo approximately fourfold volume changes during charge and discharge cycles. These volume changes cause the active material to peel away from the copper foil, which is generally used as the negative electrode current collector. This issue has hindered the widespread adoption of silicon-based active materials.
To solve this problem, I-PEX has utilized the surface treatment technology and know-how it has cultivated through the integrated production of connectors in its Connectors Business to develop an advanced conductive mesh with a three-dimensional surface structure and voids. This mesh is created by surface-treating nonwoven fabric with copper for the anode and aluminum for the cathode.
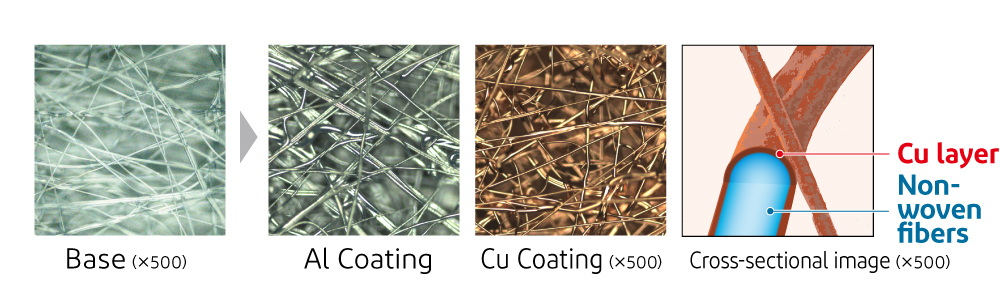 Enlarged view of advanced conductive mesh
Enlarged view of advanced conductive mesh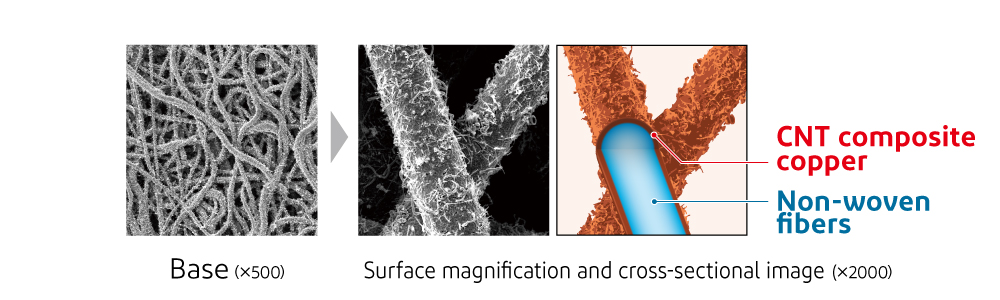 CNT composite plating on nonwoven fibers
CNT composite plating on nonwoven fibersFeatures of the Advanced Conductive Mesh
The advanced conductive mesh is expected to improve issues such as the adhesion and conductivity of silicon-based active materials in next-generation lithium-ion batteries, thereby contributing to improved battery performance
- The complex and flexible structure of the nonwoven fabric holds the active material in place, preventing peeling caused by the expansion and contraction of the silicon-based active material
- Metallization of nonwoven fabric ensures a high specific surface area of the current collector and electrical conductivity comparable to that of copper foil
- The conductive nonwoven fabric forms a conductive path throughout the active material layer, improving the utilization rate of the active material
- The current collector is made lighter by using a resin nonwoven fabric as the base material
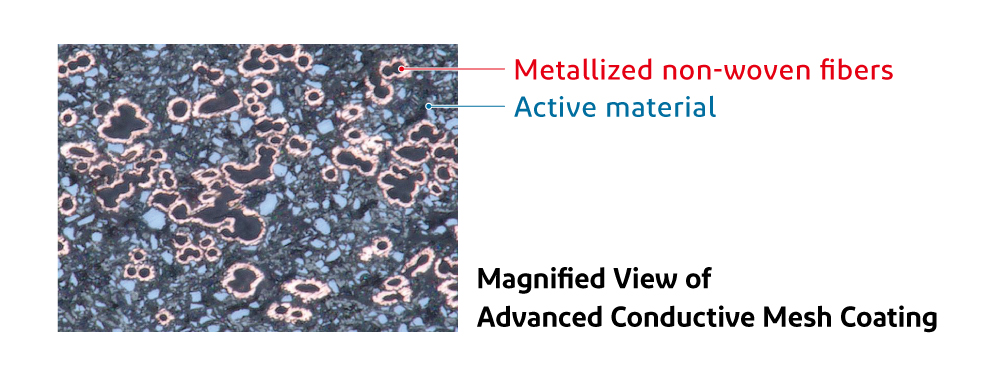 Cross-section of advanced conductive mesh
Cross-section of advanced conductive meshCycle Test Results for Advanced Conductive Mesh
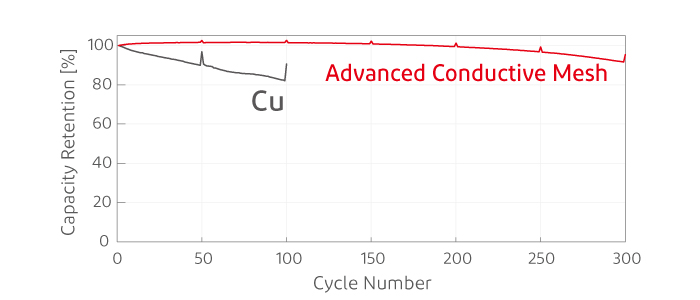 Advanced conductive mesh cycle test results
Advanced conductive mesh cycle test resultsIn this test, a lithium-ion battery with an anode containing over 65% silicon was prototyped using an advanced conductive mesh made by plating copper on nonwoven fabric, and performance was compared after 300 charge/discharge cycles. Compared with the reference copper foil, it was confirmed that the advanced conductive mesh improves cycle performance by holding the active material within the metallized nonwoven fabric fibers. It was also confirmed that the battery has good compatibility with solvent-based binders.
| Cell | Laminate Cell/Electrode (One side) |
|---|---|
| Cathode | LiCoO2 type |
| Anode | Pure Si type (Anode Capacity: ca. 2800 mAh/g) |
| Separator | Al2O3 Coated PE, 12 μmt |
| Electrolyte | 1.2M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC/FEC +Additives |
| Cell Capacity | 25 mAh (2.1 mAh/cm2) |
| Cycle Condition |
[Temp.] 25 ℃ [Charge] 0.5 C_4.2 V CC/CV 0.05 Ccut_Rest: 10 min. [Discharge] 0.5 C_CC 2.5 Vcut_Rest: 10 min. *0.2 C/0.2 C for every 50 cycles |
Specifications of the Advanced Conductive Mesh
| Substrate type | PET or PBT *1 |
|---|---|
| Thickness, basis weight | Thickness: 150-180 μm, weight: 35-50 g/m 2 *1 |
| Types of metallization | For the positive electrode: aluminum, for the negative electrode: copper *2 |
| Addition of CNTs | Our patented CNT composite copper plating technology allows CNT to be attached to the fiber surface. |
- *1Requests can be considered
- *2Other materials such as nickel, tin, and precious metals can be considered upon request
Download Catalogue
Exhibition Overview
The advanced conductive mesh will be exhibited at the "66th Battery Symposium Exhibition" to be held at Winc Aichi from Tuesday, November 18th to Thursday, November 20th, 2025.
| Dates | November 18th (Tuesday) - 20th (Thursday), 2025 |
|---|---|
| Place | Winc Aichi (Nakamura Ward, Nagoya City) Booth number: 6F No.15 |
| Exhibit Products | Advanced conductive mesh |
For details on the 66th Battery Symposium and Exhibition, click here
About I-PEX's Energy Solutions Business
I-PEX has developed the "RENERATH" series of battery storage systems, which reuse used lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles. By combining reused batteries with IoT technology, the company aims to provide a sustainable, safe, and secure energy supply through storage batteries. As a new initiative in energy solutions, the company is currently developing advanced conductive mesh for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.
Click here for details on Battery Storage System
About I-PEX Inc.
I-PEX stands for “Innovative Product development & Engineering solutions eXpert” providing value in the form of inspiration and astonishment in the global marketplace. The company was founded in 1963 as Dai-ichi Seiko, a precision mold manufacturer, and has since produced numerous world-firsts and unique products and solutions. I-PEX currently operates in five business fields: Connectors, Contract Manufacturing (Automotive Components & Electronics Components), Molds & Equipment, MEMS Foundry, and Energy Solutions. By delivering the sharpest tip to the world, we will contribute to exciting value-creation in the digitalized society by working globally with every customer who opens up the new era.
| Trade Name |
I-PEX Inc.
|
|---|---|
| President |
Representative Director and President, Reiji Konishi
|
| Location |
12-4, Negoro, Momoyama-cho, Fushimi-ku, Kyoto 612-8024, JAPAN
|
| Establishment |
July 10, 1963
|
| Paid-in Capital |
10.968 billion yen (as of December 31, 2024)
|
| Business Operation |
|
| URL |